AC vs. DC Charging: It’s All About Conversion 🔄
No matter the type, your EV’s battery speaks only one language: DC. So what makes AC and DC charging different?
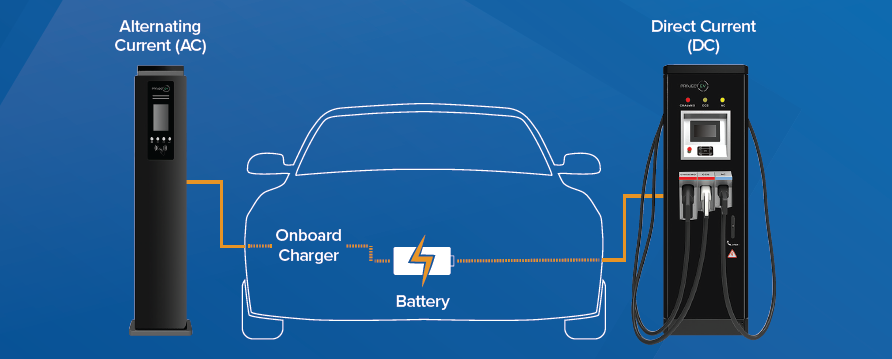
🔋DC Charging Stations: Here, the heavy lifting is done outside your EV. These stations convert AC to DC *before* the power reaches your car, allowing for rapid charging as they can house larger conversion equipment. Think of it as a fast-food drive-thru for your EV – quick and efficient.
🚗 AC Charging: This is more of a home-cooked meal approach to charging your EV. Your vehicle’s onboard charger takes care of the AC to DC conversion, which means the process is generally slower as the chargers are designed to fit within your car’s limited space.
But why does this matter?
Knowing the difference can help you plan your charging strategy effectively, especially if you’re a frequent traveller or considering the infrastructure for your business. It’s not just about plugging in; it’s about making informed decisions that save you time and suit your lifestyle. The trend is clear: charging infrastructure is diversifying to accommodate various needs, from lightning-fast DC stations for on-the-go top-ups to the convenience of overnight AC home charging
EV Plug Types
Unlike traditional internal combustion engine cars that all use similar filler nozzles to receive their fill of fuel, with electric cars there are at least four different plugs types, with various manufacturers committed to one or even two variations, so it’s important to know your vehicle plug types. For AC charging there are two types of plugs you need to know, these are known as Type 1 & Type 2 plugs (nice and simple). For DC charging there are also two types of plugs you need to know, these are known as CCS & CHAdeMO plugs.
As catchy as the name CHAdeMO is, it is actually derived from the Japanese phrase “O cha demoikaga desuka” which translates as, “Would you like some tea?”, signifying it charges as quickly as it takes to have a cup of tea.
For more information: ERF Sustainability Guide